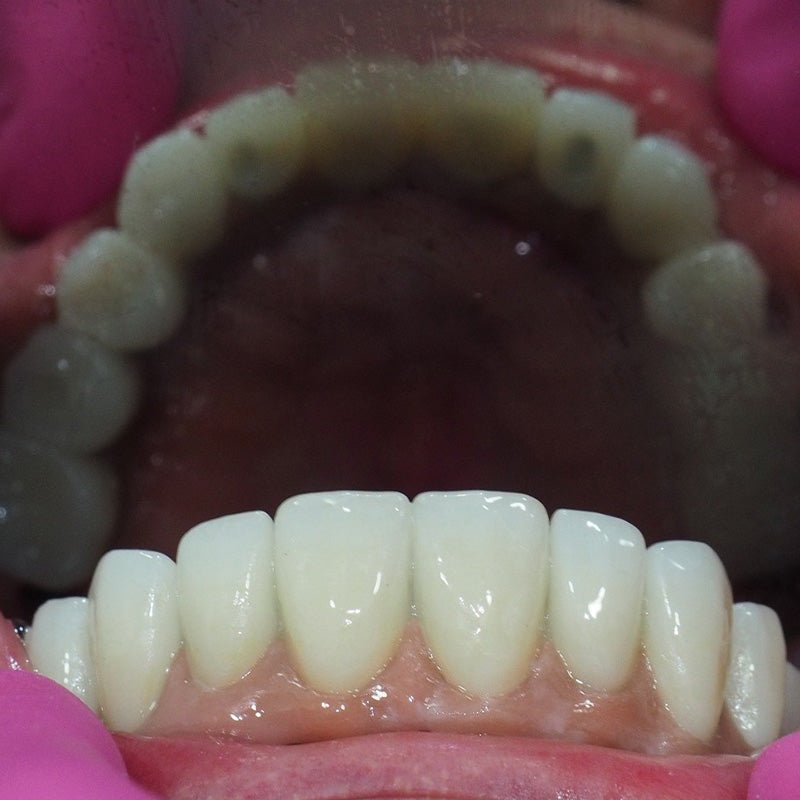
Zirconia, or zirconium dioxide, is a high-strength ceramic material that offers excellent compatibility with human tissue, making it an ideal choice for creating durable, aesthetically pleasing dental restorations.
This comprehensive guide delves into all aspects of dental zirconia blocks, exploring their properties, varieties, usage guidelines, and advantages to provide a deeper understanding of this innovative dental tool.

Properties of Dental Zirconia
Zirconia is a crystalline dioxide of zirconium, renowned for its toughness and resistance to cracks. These characteristics primarily stem from its unique phase transformation and toughening mechanism. When stress is applied, zirconia can switch from a tetragonal phase to a monoclinic phase, this transformation often occurs to compensate for stress. Furthermore, zirconia exhibits excellent biocompatibility, making its interaction within the body favorable.
As a whole, dental zirconia stands as the toughest ceramic material utilized in modern dentistry. Its power, coupled with exceptional aesthetic properties, sets the stage for its usage in a broad range of dental restorations.

Types of Dental Zirconia Blocks
Dental zirconia blocks come in various types, catering to diverse patient needs. The three most common types include:
1. High Translucent Zirconia: These blocks have increased translucence to mimic the appearance of natural teeth more accurately, typically used in anterior restorations, veneers, inlays, and onlays.
2. Solid Zirconia: This type is less translucent but shows higher strength for more substantial restorations, generally used for posterior restorations or bruxers.
3. High-Strength or 3Y Zirconia: 3Y Zirconia blocks contain 3 mol% yttria and undergo a process of partially stabilized zirconia, giving them the highest strength for demanding applications.

Hidden Secrets to Success in CAD/CAM Milling
Zirconia restorations are typically milled using a CAD/CAM system, allowing for precise, convenient, and efficient restoration fabrication. For best results, the following factors are crucial:
1. Understanding the Material: A comprehensive understanding of the zirconia’s properties, types, uses and limitations can enhance procedural success.
2. Digital Precision: The beauty of CAD/CAM technology lies in the precision it offers. This allows dental professionals to mill restorations with excellent marginal fits.
3. Post-Processing Procedures: Once milled, the zirconia restoration must undergo a sintering process to reach its final hardness and color. Proper sintering is quintessential to the restoration's success.
From Dental Lab to Oral Applicability
Dental zirconia blocks are used to fabricate a variety of restorations:
1. Crowns: Both full-contour and porcelain-layered zirconia can be used to fabricate crowns that can withstand high occlusal forces while effectively mimicking the appearance of natural teeth.
2. Bridges: Due to its tremendous tensile strength, zirconia can be efficiently used in multi-unit bridges, even in the posterior region.
3. Implant Restorations: Zirconia is resistant to corrosion, making it a suitable material for fabricating long-lasting, aesthetically pleasing implant restorations.
4. Inlays, Onlays and Veneers: Zirconia's excellent biocompatibility and superior aesthetic characteristics make it an ideal choice for conservative restorations like inlays, onlays, and veneers.

Advantages of Using Dental Zirconia Blocks
Numerous advantages of dental zirconia blocks have led to their widespread acceptance in dentistry:
1. Strength and Durability: Zirconia is famed for its toughness, surpassing that of traditional porcelain and acrylic resins, resulting in restorations that withstand mechanical stress significantly.
2. Aesthetics: High-translucent zirconia closely mimics the appearance of natural teeth, enhancing the overall aesthetic outcome.
3. Biocompatibility: Zirconia presents excellent biocompatibility, resulting in little to no irritation to the surrounding tissue.
4. Efficiency: CAD/CAM technology expedites the fabrication process of zirconia restorations, providing a quicker turnaround time.
5. Versatility: Due to different types of zirconia blocks and their distinct properties, they can be used for a wide range of restorations.
Conclusion
Taking a 360-degree inspection of the world of dental zirconia blocks, it is apparent that this groundbreaking technology has truly revolutionized the field of restorative and aesthetic dentistry. Its transformative attributes have set a firm benchmark in dental restoration. By offering superior strength, natural appearance, biocompatibility, and versatility, dental zirconia blocks are a testament to how advanced technology can enhance the art of dentistry. However, understanding the nuances of zirconia blocks and applying them appropriately is paramount to capitalizing upon their potential and paving the way for successful restorations.